'Uganda's Tale of COVID-19, Medicine, and Vaccination' and 'Vietnam's Tale of COVID-19, Medicine, and Vaccination'
Uganda's Tale of COVID-19, Medicine, and Vaccination
Pandemic National Case Studies
"He who loves you, loves you with your dirt." -Ugandan proverb
The Central African nation of Uganda, a country of more than 45 million people, saw only 40 cases of COVID-19 through the end of March, 2020. Concerned about the potential for a more substantial outbreak of the fast-spreading coronavirus, Uganda jumped on the quickly-growing hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) HCQ bandwagon, most often using it as part of a multi-drug regimen in combination with azithromycin, zinc, vitamin C and vitamin D. Through mid-July, Uganda had seen over 1,000 cases of COVID-19 without a single fatality---the largest such "perfect record" in the world at that point in time.
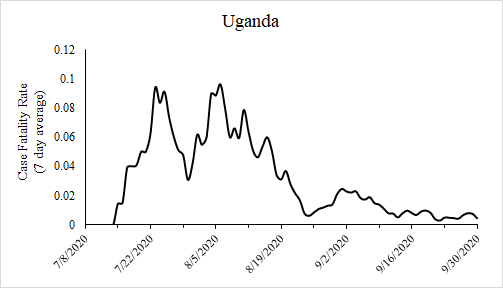
In late July, citing the World Health Organization's claim of HCQ's lack of efficacy, Uganda dropped HCQ as their standard of care for COVID-19 patients. After that decision, during the last eight days of July, Uganda saw its first six COVID-19 fatalities. The cases were not growing so fast as the deaths as Uganda's case fatality rate (CFR) skyrocketed from the lowest level in the world to among the very highest at nearly 10%.
While it is unclear why a nation handling the pandemic so well would change treatment policy, it may be noteworthy that Uganda received millions of dollars from each the World Bank, the African Development Bank, and the International Monetary Fund, and that totaled more than $1 billion dollars, each within a few days of the decision. Most of that aid came in the form of loans, which angered many Ugandans.
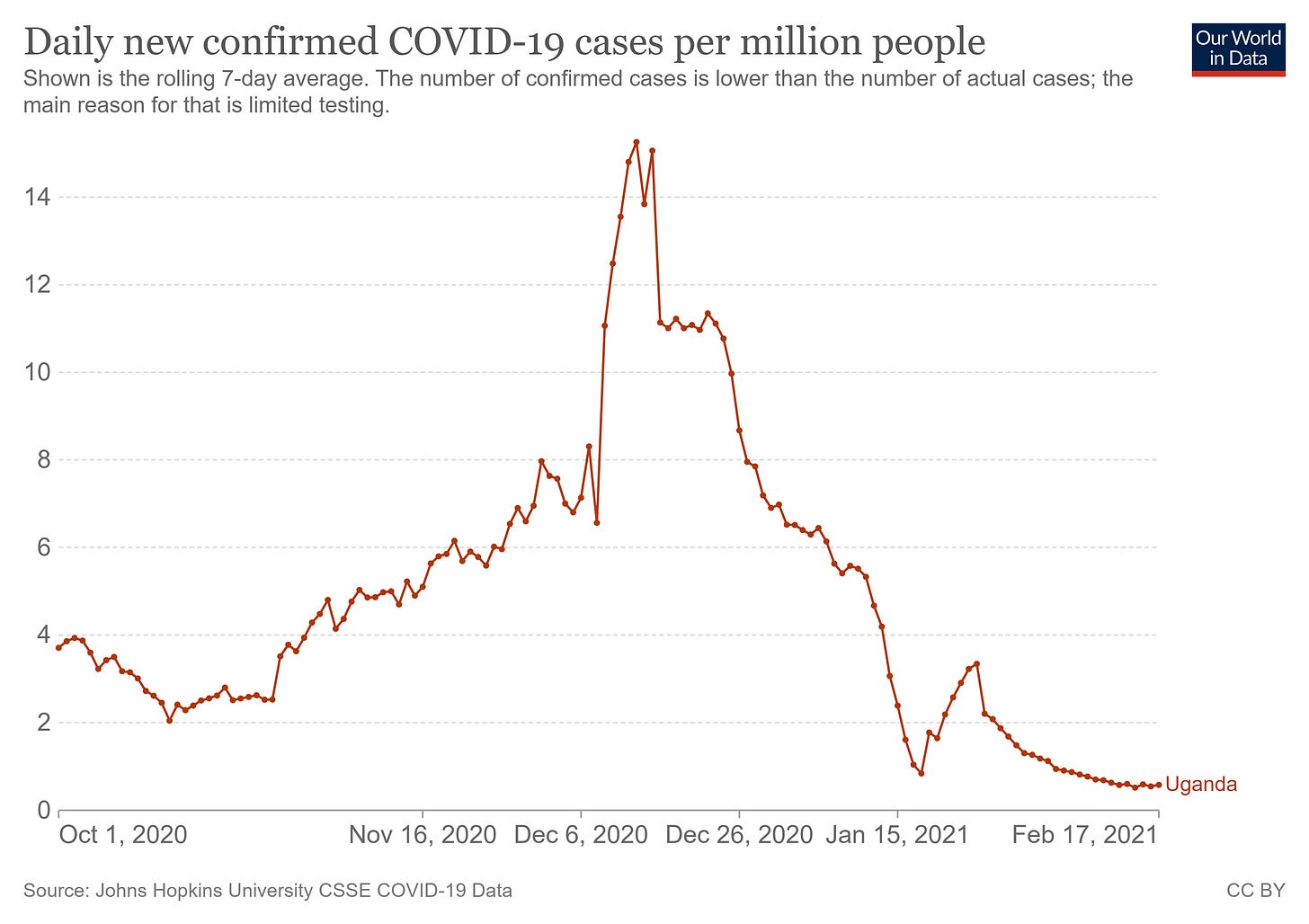
In mid-October, the Daily Monitor declared, "New drug to curb rising COVID-19 deaths," as the expensive remdesivir got approved for treatment in Uganda. It sometimes seems strange how media outlets believe they know the results before they happen. However, Uganda saw cases and deaths climb for weeks afterward.
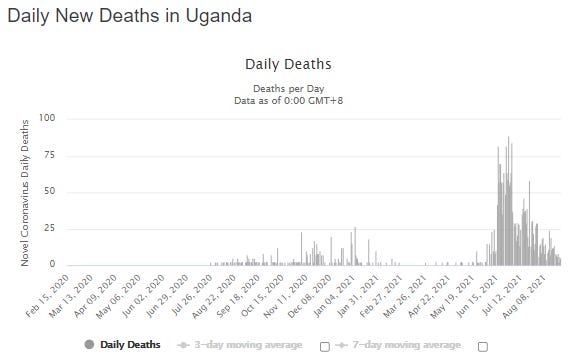
More recently, Uganda began its vaccination campaign on March 10, 2021. Since then, the CFR has once again jumped up above world averages, somewhat similar to what happened throughout Europe during the early days of its vaccine campaign. Uganda has only vaccinated around 2% of its population, and that small portion far more gradually than did Europe. However, since the outset of Uganda's vaccination campaign, total COVID-19 deaths have jumped from 568 to around 3,000 as of August 27, 2021.
Vietnam's Tale of COVID-19, Medicine, and Vaccination
Pandemic National Case Studies
“One worm may damage the whole cooking soup.” -Vietnamese Proverb
TUBS, CC BY-SA 3.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
Sharing a border with China, the ostensible source of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, Vietnam was the ninth nation to announce a confirmed infection on January 24, 2020. Unlike any of the nations that saw an outbreak before them, Vietnam managed to escape the impact of COVID-19, recording barely 500 cases and no deaths until July 31, 2020. As early as February 20, Vietnamese medical officials announced the “development of an effective treatment”. While stating that the treatment did not depend on a single medicine that could cure patients alone, Vietnamese pharmacies were swamped with purchases in March and the Ministry of Health soon began the process of registering a trial for chloroquine (CQ), which China also selected as its drug of choice for COVID-19 patients on February 19.
It is unclear to me the exact date on which Vietnam stopped using CQ, though this article on August 4 relays the decision:
The information was announced by Nguyen Van Kinh, former Director of the National Hospital for Tropical Diseases and chairman of Vietnamese Society of Infectious Disease, as he discussed the latest revision of the health ministry’s COVID-19 diagnosis and treatment guidelines (the fourth comprehensive update since the coronavirus cases were first recorded in Vietnam in late January).
The health ministry noted that while there had not been a definitive drug to treat COVID-19, a variety of antiviral drugs – including the domestically available lopinavir, ritonavir and interferon – might deliver some results as many patients were cleared of the virus within a week.
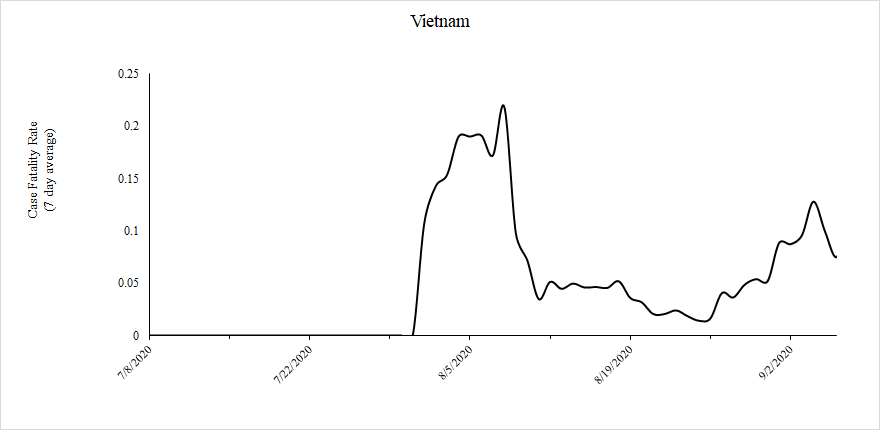
Vietnam outlasted Uganda’s perfect record by a week, reporting its first death from COVID-19 on July 31, 2020, coincidentally the same day it was reported that they received millions of dollars from the World Bank to help “cope with COVID-19”. From that moment, Vietnam’s case fatality rate climbed from 0% to around 20%. It is noteworthy that for some reason Our World in Data does not allow users to view the CFR graphs prior to September 1, 2020, even though the data that would be used to do it is available.
Fortunately, the death toll ended in early September in Vietnam, though cases trickled in by a few dozen per week for a few months.
Vietnam’s COVID-19 Vaccine Campaign
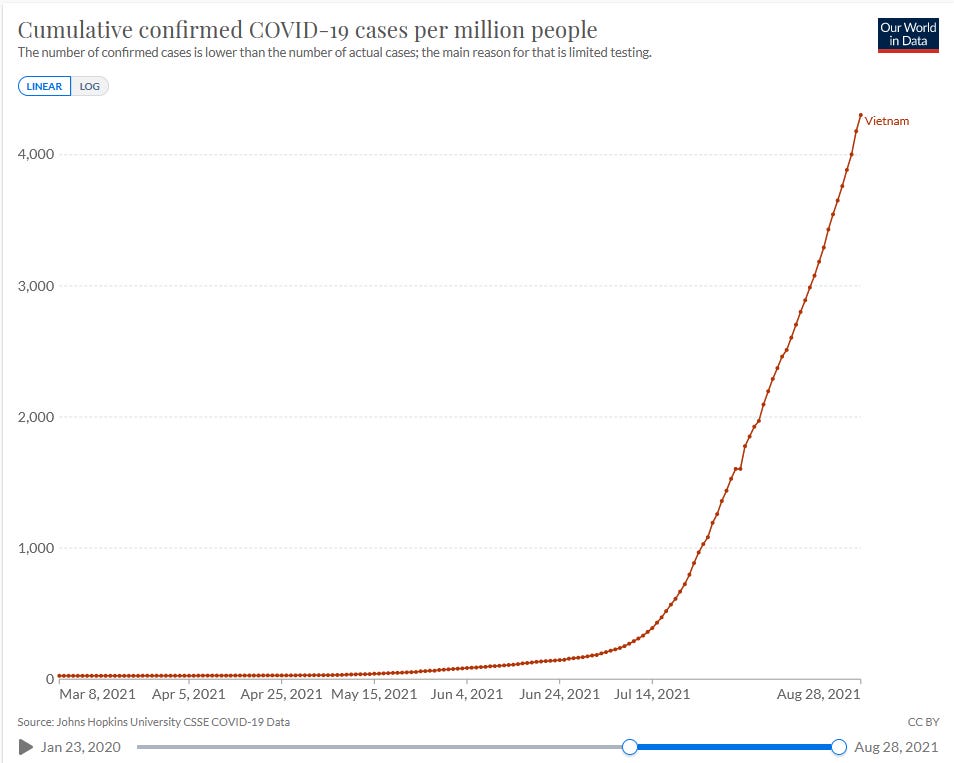
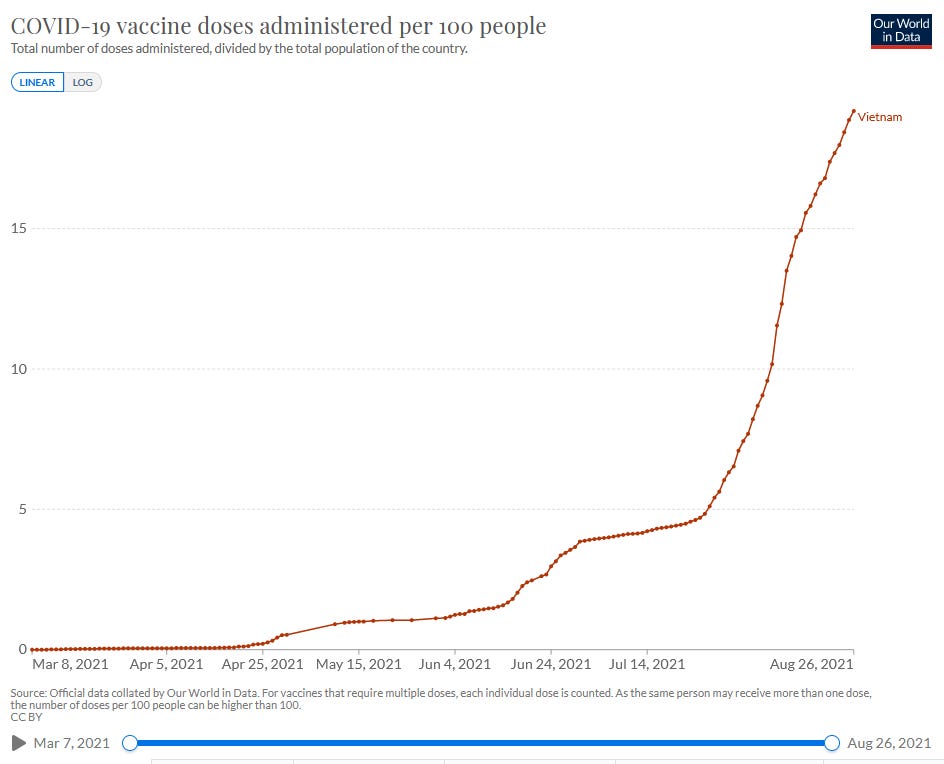
Vietnam began its vaccination campaign on March 8, 2021 after not having suffered a COVID-19 fatality in over six months. Starting with the AstraZeneca vaccine, Vietnam quickly approved Russia’s Sputnik V for use starting 15 days later. For more than two months into the vaccination campaign, Vietnam still reported no new COVID-19 fatalities. Then the situation began to change---slowly at first, and only recently looking to begin to peak at over 200,000 active cases. In the nation that had recorded just 35 COVID-19 deaths prior to May 15, 2021, the death toll currently stands at over 10,000 and will likely head toward 20,000 by the end of September, assuming the situation doesn’t worsen.
Few Vietnamese were vaccinated during the early part of the campaign. Though Chinese vaccines were added to the list of options, anti-Chinese sentiment is reported to have led some Vietnamese to wait for the availability of other brands. U.S. vaccines from Pfizer, Moderna, and then Johnson & Johnson were approved on June 12, June 29, and July 15, respectively, with millions of doses shipped to Vietnam. By late July, Vietnam’s SARS-CoV-2 infection rate soared like never before.
By the end of May, it was reported in news outlets that a new SARS-CoV-2 variant had emerged in Vietnam. We can add that to the essentially complete list of variants of interest that emerged after the introduction of vaccines to a population. A study published in The Lancet (Chau and Ngoc, 2021) on August 10, 2021 notes the association of the emergent variant with breakthrough cases involving “low-levels of vaccine-induced neutralizing antibodies” among health care workers who may very well have precipitated the ongoing epidemic.
The Curious View From the West
Looking back at Vietnam’s relative success with COVID-19 during 2020, consider stories like this one told by the Western media. There is not a single mention of CQ, though the author talks about Vietnam’s younger population, then waxes poetically about the success of localized and targeted public health surveillance. However, while variables like CQ and vaccines changed, and we can judge the results as natural experiments, there is no evidence that the case trackers stopped trying to do their jobs. CNBC suggests that Vietnam “punched above its weight” using large-scale quarantines and closing borders. Somehow, those tactics don’t seem to be holding up now.
Comments
Post a Comment